Purpose of Accounting ALOE Equation & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript
Как выберет Онлайн-казино Руководство по Казин
August 9, 2024Sport Madaniyati Sayfa A Couple Of 2 So’nggi Tendentsiyalarni Ko’rib Chiqish Se Till Att Du Är Tahlil Qilis
September 8, 2024
CI (Certificate of incorporation) – A document filed with a state government to create a corporation. CFO (Chief financial officer) – The senior executive in a company responsible for managing its financial affairs. CDS (Credit default swap) – A financial contract that protects against the default of a debt issuer. BR (Balance rate) – The interest rate charged on a loan or note when the debt balance is not paid in full. ALCO (Asset-liability committee) – A committee of a bank’s management that reviews and approves the bank’s lending and borrowing policies.
Return on Investment (ROI)
A calculation that measures a company’s average cost of capital from all sources, including common stock, preferred stock, and debt. It represents the minimum return a company must earn on its existing asset base to satisfy its investors. The current tax depreciation system in the United States, which allows businesses to recover the cost of certain tangible property through annual deductions. MACRS provides guidelines for determining the depreciation schedule and methods that can be used to deduct the cost of various types of assets. Also known as a statement of owner’s equity or statement of stockholders’ equity, it shows changes virtual accountant in the equity accounts on the balance sheet, including stock issuances, repurchases, and dividend payments.

What are trade creditors?
- This is double-entry bookkeeping so we need to make a second entry of the same amount.
- FIFO (First in, first out) – A method of inventory accounting that assumes that the first items to be added to inventory are also the first items to be sold.
- These are long-term investments that are expected to produce benefits over multiple years.
- Money in to your credit card account is directly linked to a nominal code.
Simple, jargon-free explanations of accounting terms for small business owners. The extent of accounting, as it was in before days, has gone through heaps of changes lately. As it is a unique subject, its degree and region of activity have been continually expanding staying up with the progressions in financial changes.
Balance Sheet (BS)
In this way, it tends to say that simply keeping records can be the essential target of any individual or element. Then again, the principle objective might recognize as taking choices dependent on monetary data provided by accounting. Subsequently, they themselves certainly not even hand, it assists with accomplishing a particular goal. So it says the accounting is an unfortunate obligation’ and it isn’t ‘an end in itself’. Determines the present value of the expected future cash flows from an investment or project, discounted back to the present at an appropriate discount rate.

ROE (Return on equity) – A measure of how profitable a company is relative to the money that shareholders have invested in it. ROA (Return on assets) A measure of how profitable a company is relative to its total assets. MTM (Mark-to-market) – Mark-to-market accounting is a method to determine the value of an asset that can fluctuate over time. LTL (Long-term liabilities) – The company’s debts to third-party creditors that can be paid beyond 12 months.
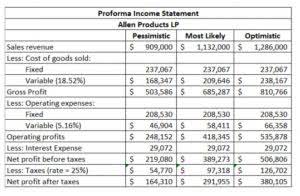
Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR)

AGI (Adjusted gross income) – One of the most critical accounting acronyms signifies a taxpayer’s total income minus certain deductions and exemptions. While accounting is all about numbers, they are not the only thing that matters to keeping your books in order. So, let’s take a break from the numbers and look at some letters known as accounting abbreviations. We’ve listed the most important ones and some helpful financial glossary below to help you stay on top of your accounting operations. Assets are on the top or left, and below them or to the right are the company’s liabilities and shareholders’ equity. A balance sheet is also always in balance, where the value of the assets equals the combined value of the liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
This is a profitability measure that indicates a company’s operating performance. It excludes the effects of financing and accounting decisions (interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). A special type of corporation in the United States that elects to pass corporate income, losses, deductions, and credits through to its shareholders for federal tax purposes to avoid double taxation. For clarification, double taxation is where corporate income is taxed at the corporate level and again when distributed to shareholders as dividends. The financial snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at retained earnings a specific time. WACC (Weighted average cost of capital) – The average cost of financing company’s assets, weighted by the amount of debt and equity each type of financing represents.
- APA (Accounting principles applied) – A set of accounting standards for financial statements.
- ACCT is one of the accounting acronyms that could have a double meaning since it can also be used as an abbreviation for accountant.
- PBC (Professional body corporate) – A type of business entity used in certain countries outside the United States.
- LLCs are a popular choice for small businesses and startups in the United States.
- In some jurisdictions, summary financial statements are available (or may be required) on a quarterly basis.
- The IFRS Foundation is a not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
- CA (Cash accounting) – A method of accounting in which revenue and expenses are recorded when cash is received or paid.

It implies that all assets are financed either by borrowing money (liabilities) or by using the owner’s money (equity). In other words, the performance obligation of the company has not yet been met. The cash payment collected from the customer was received in advance because the company is obligated to provide a specified benefit to the customer on a future date. Each specific contractual obligation contained within the customer contract (and the corresponding pricing and performance obligation) determines the timing of the revenue recognition. In effect, ASC 606 provided a more what does aloe stand for in accounting robust structure for revenue accounting for public and non-public companies, which, most importantly, became standardized across all industries. Under ASC 606, companies are directed to recognize revenue in the period in which the good or service is transferred to the customer (and thus, “earned”).

